What is Data?
- Data is a
collection of raw, unorganized, unstructured facts and details - Like text, observations, figures, symbols, and descriptions of things etc.
- Data
doesn’t have any meaningunless processed. - Types of Data
- Quantitative
Numerical form- Weight, volume, cost of an item.
- Qualitative
Descriptive, but not numerical- Name, gender, hair color of a person.
- Quantitative
What is Information?
Information is meaningful data- It is
processed, organized, and structured data - It provides context of the data and enables decision making.
- Processed data that make sense to us.
- Information is extracted from the data, by analyzing and interpreting pieces of data.
- E.g.,you have data of all the people living in your locality, its Data, when you analyze and interpret the data and come to some conclusion that:
- There are 100 senior citizens.
- The sex ratio is 1.1.
- Newborn babies are 100.
Data vs Information
- Data is a collection of facts,
- while information puts those facts into context.
- While data is raw and
unorganized- information is organized.
- Data points are individual and sometimes unrelated.
- Information maps out that data to provide a big-picture view of how it all fits together.
- Data, on its own, is
meaningless- When it’s analyzed and interpreted, it becomes meaningful information.
- Data does not depend on information;
- however, information depends on data.
- Data typically comes in the form of graphs, numbers, figures, or statistics.
- Information is typically presented through words, language, thoughts, and ideas.
- Data isn’t sufficient for
decision-making- but you can make decisions based on information.
What is Database?
- Database is an electronic place/system where
data is storedin a way that it can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. - It is also used to
organize the datain the form of a table, schema, views, and reports, etc.
What is Database management system(DBMS)?
- DBMS is a software which is used to manage the database. For example: MySQL, Oracle, etc
- The primary goal of a DBMS is to provide a way to
store and retrievedatabase information that is bothconvenient and efficient - It
provides protection and securityto the database. - In the case of multiple users, it also maintains data consistency.
DBMS vs File Systems
- File-processing systems has major disadvantages
Data Redundancy and inconsistency- Difficulty in accessing data
- Data isolation
- Integrity problems
Atomicityproblems- Concurrent-access anomalies
Securityproblems
- Above 7 are also the Advantages of DBMS (answer to “Why to use DBMS?”)
View of Data (Three Schema Architecture)
- The major purpose of DBMS is to provide
- an
abstract viewof the data. hides certain detailsof how the data is stored and maintained.- to
simplify user interaction - multiple users to access the same data with a
personalized view
- an
- The collection of information stored in the DB
at a particular moment is called an instance of DB - The
overall design of the DB is called the DB schema - Schema is structural description of data.
- Schema doesn’t change frequently.
- Data may change frequently.
We have 3 types of Schemas: Physical, Logical, several view schemas called subschemas.
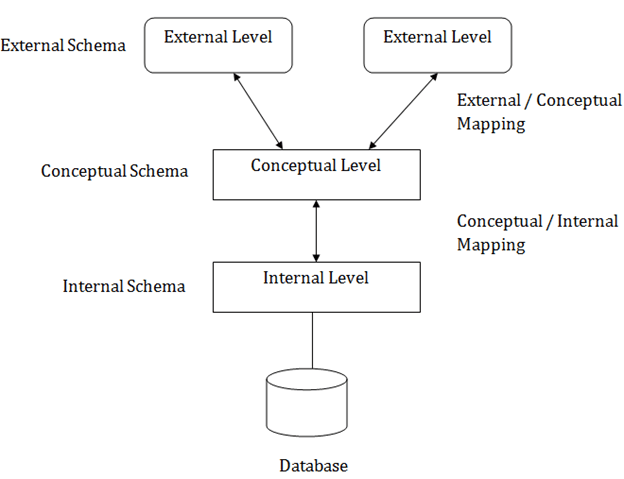
-
Physical level / Internal level
- The
lowest level of abstractiondescribeshow the data are stored - It has Physical schema which describes physical storage structure of DB.
- Talks about: Storage allocation (N-ary tree etc), Data compression & encryption etc.
- Goal: We must define algorithms that allow efficient access to data.

- The
-
Logical level / Conceptual level
- The conceptual schema describes the
design of a databaseat the conceptual level, describeswhat data are stored in DB, and what relationships exist among those data. - User at logical level does not need to be aware about physical-level structures.
- DBA, who must decide what information to keep in the DB use the logical level of abstraction.
- Goal: ease to use.

- The conceptual schema describes the
-
View level / External level
Highest level of abstractionaims to simplifyusers’ interactionwith the system by providing different view to different end-user.- Each view schema describes the database part that a particular user group is interested and hides the remaining database from that user group.
- At the external level, a database contains several schemas that sometimes called as subschema.
- The subschema is used to describe the different view of the database.
- At views also
provide a security mechanismto prevent users from accessing certain parts of DB.
Database Languages
- Data definition language (DDL)
- DDL is used to
specify the database schema - We specify consistency constraints, which must be checked, every time DB is updated.
- DDL is used to
- Data manipulation language (DML)
- DML is used to express
database queries and updates - Data manipulation involves
- Retrieval
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Updating
- Query language, a part of DML to specify statement requesting the retrieval of information.
- DML is used to express
- Practically, both language features are present in a single DB language, e.g., SQL language.
How is Database accessed from Application programs?
- Apps written in host languages, C/C++, Java interacts with DB.
- E.g., Banking system’s module generating payrolls access DB by executing DML statements from the host language.
- An
interface in implementedbetween the App and DB - API is provided to send DML/DDL statements to DB and retrieve the results.
- Open Database Connectivity (ODBC), Microsoft “C”.
- Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), Java.
Database Administrator (DBA)
A person who has central controlof both the data and the programs that access those data.- It works on logical level
- Functions of DBA
- Schema Definition
- Storage structure and access methods.
- Schema and physical organization modifications.
- Authorization control.
- Routine maintenance
- Periodic backups.
- Security patches.
- Any upgrades.
DBMS Architecture
- A DBMS architecture allows
dividing the database systeminto individual components that can be independently modified, changed, replaced, and altered. - The DBMS architecture affects the performance of the database
- It describes the structure and the way in which the users are connected to a specific database system.
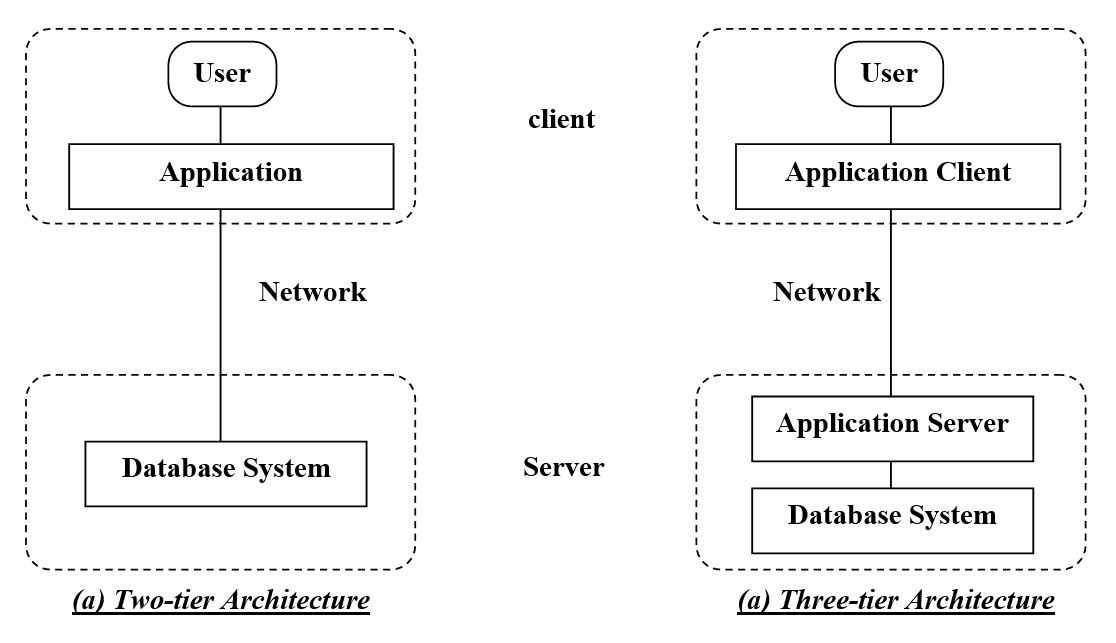
- Tier-1 Architecture
- It is the simplest architecture of Database
- The client, server & DB
all present on the same machine
- Tier-2 Architecture
- App is partitioned into
2-components - Connection to
DB is through network- SQL queries travels through network
- App is partitioned into
- Tier-3 Architecture
- App is partitioned into
3 logical components - Client machine communicates with App server, and App server communicated with DB system to access data.
- Client machine –> is just a frontend
- App server –> Business logic
- T3 architecture are best for WWW Applications.
- Advantages:
Scalabilitydue to distributed application servers.Data integrity, App server acts as a middle layer between client and DB, which minimize the chances of data corruption.Security, client can’t directly access DB, hence it is more secure.
- App is partitioned into