# Topic covered
* Software Engineering
* History of software engineering
* Software Development Life Cycle(SDLC)
* SDLC Phases
* SDLC Models
* Classical Waterfall model
* Iterative Waterfall Model
* Prototype Model
* Incremental Model
* Spiral Model
* Agile Model
1. Software Engineering
Software Engineering is related to the evolution of software product using well-defined scientific principles, techniques, and procedures.
The result of software engineering is an effective and reliable software product.
- Need of Software Engineering
- To
manage Large software - For better
Scalability,CostManagement,Quality
- To
1.1 History of software engineering
- 1940 - 50
- Simple software development started by big giant like IBM, NASA, etc
- Build and Deliver methods used
- 1945 to 1965 –>
The origins- Introduces by NATO Science Committee
- 1965 to 1985 –>
The software crisis- Many software projects failed.
- Due to over budget, expensive to maintain, late delivery…
- Eg: IBM OS/360
- 1990 - 1999 –>
Prominence of the Internets- World Wide Web, OS
- 2000 - 2010 –>
Lightweight methodologies - 2010 - Till –> AI, ML, DL
1.2 Software Development Life Cycle(SDLC)
- SDLC is a systematic, disciplined, cost-effective
techniques for software development - SDLC process aims to produce
high-qualitysoftware that meetscustomer expectations - SDLC consists of a
detailed infowhich explains how to plan, build, and maintain specific software.
1.3 Why SDLC?
- It offers a basis for
project planning, scheduling, andestimating - Provides a
frameworkfor a standard set of activities and deliverables - It is a mechanism for
project trackingand control - Increases visibility of project planning to all involved stakeholders of the development process
- Increased and enhance
development speed - Helps you to
decrease project riskand project management plan overhead
1.4 SDLC Phases

- Requirement Gathering and analysis
- This includes calculating labor and material
costs, creating atimetablewith target goals, and creating the project’steams and leadershipstructure.
- This includes calculating labor and material
- Feasibility study
Define and document the software needs–> known asSRS Document(Software Requirements Specification)- 5 Checks: Economic, Legal, Operation feasibility, Technical, Schedule
- Design
- The
system and software design documentsare prepared as per the SRS document. - All High-Level Design (
HLD) and Low-Level Design (LLD) document are prepared.
- The
- Coding
- It is the
longest phaseof the Software Development Life Cycle process.
- It is the
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Bug fixing– bugs are reported because of some scenarios which are not tested at allUpgrade– Upgrading the application to the newer versions of the SoftwareEnhancement– Adding some new features into the existing software
1.5 SDLC Models
1.5.1. Classical Waterfall model
- It is very simple but
idealistic - Earlier this model was very popular but nowadays it is
not used - But it is very important because all the
other sdlc models are based on the classical waterfall model - Basic, Rigid, Inflexible, Not for real project
The outcome of one phase acts as the input for the next phase. i.e. development process can be considered as a sequential flow
Pros
* Base Model
* Simple and easy
* For smaller projects
Cons
* No feedback path
* Sequential flow

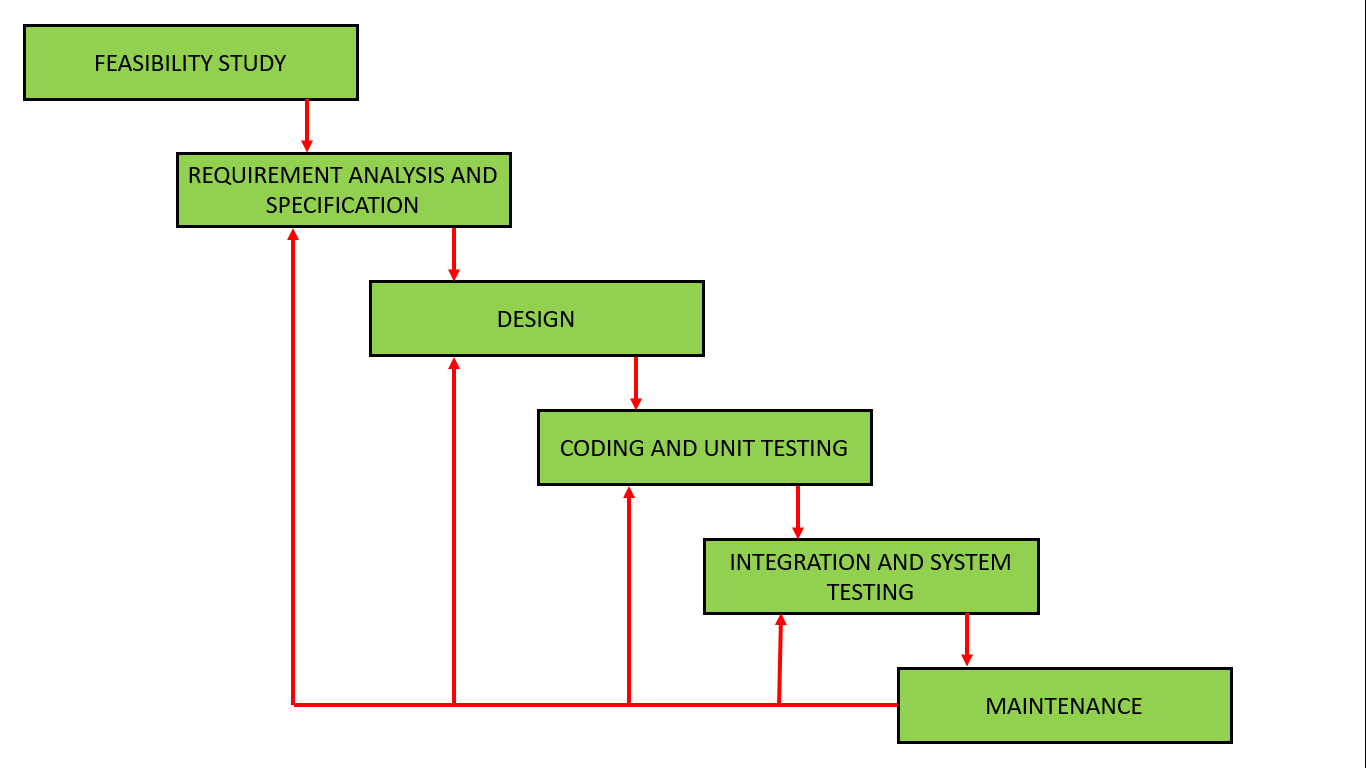
1.5.2. Iterative Waterfall Model
- Basic, Problem should be well understood
The iterative waterfall model provides feedback paths from every phase to its preceding phases
Pros
* Simple and easy
* For smaller projects
* Feedback path
Cons
* Sequential flow
* No Incremental delivery
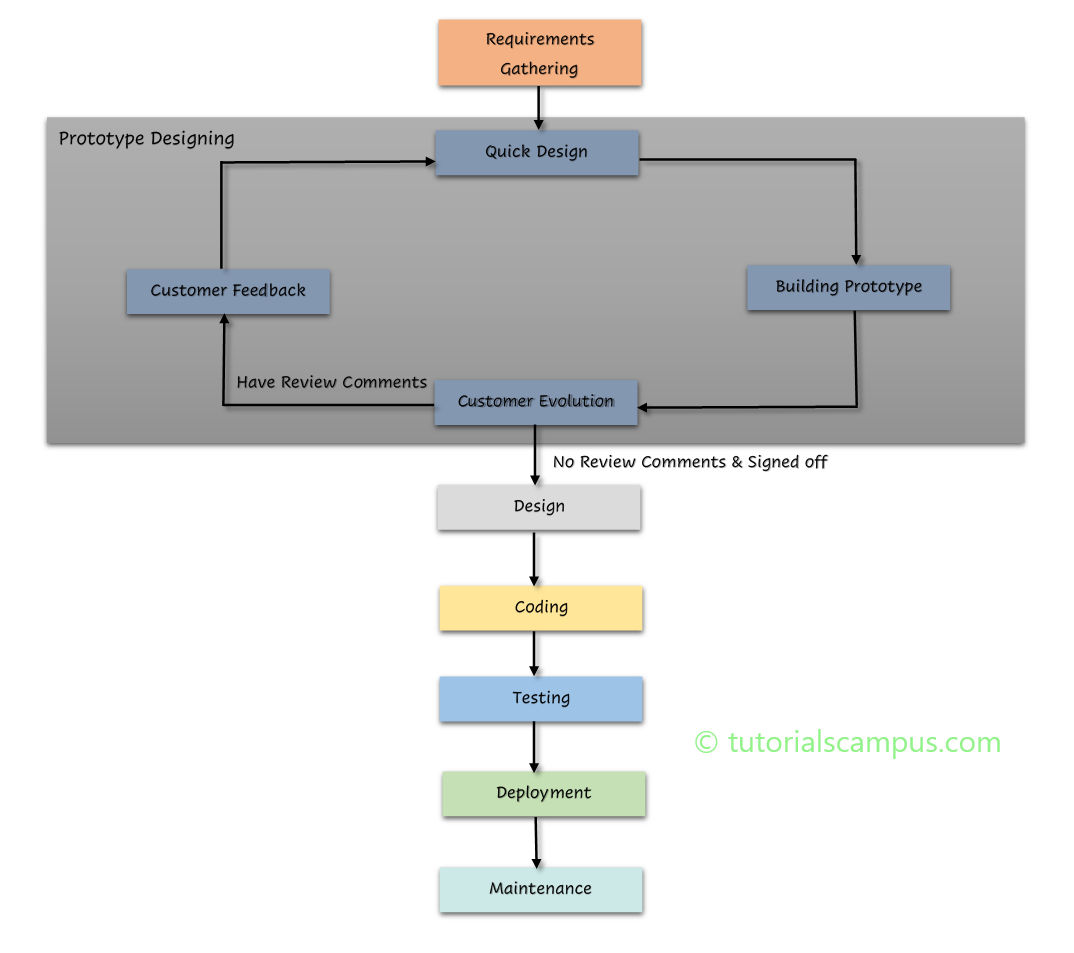
1.5.3. Prototype Model
- Used where user
requirement is not clear, Costly
In prototype model, before carrying out the development of actual software, a working prototype of the system is built
Pros
* Reduce the risk of incorrect user requirement
* Support early product marketing
Cons
* Prototyping building can be expensive
* Special tools & techniques are required to build a prototype
* It is a time-consuming process
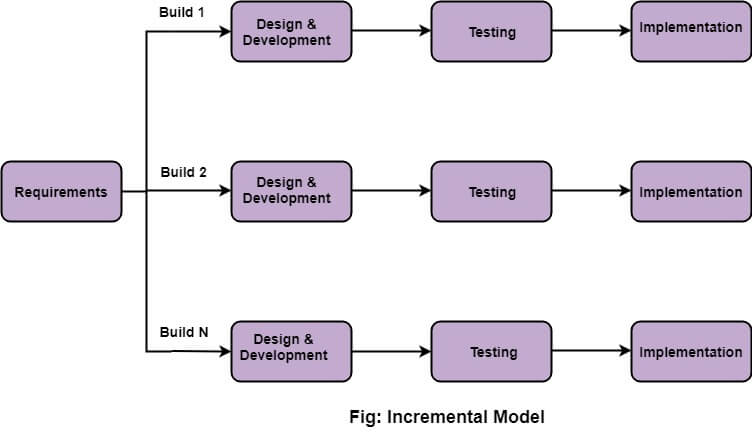
1.5.4. Incremental Model
- Incremental Model is a process where requirements
divided into multiple standalone modules - Module by module delivery, easy to test and debug
Pros
* Errors are easy to be recognized
* Easier to test and debug
* Initial cost is low
* The client gets important functionality early.
Cons
* Total Cost is high
1.5.5. Spiral Model
- Spiral Model is
used for risk managementthat combines the iterative - Risk analysis, Big project, not early lock requirement
Pros
* Risk Handling
* Good for large projects
* Flexibility in Requirements
Cons
* Complex
* Expensive
* Too much dependability on Risk Analysis

1.5.6. Agile Model
- Agile Model is
combination of iterative and incrementalprocess models - It focuses on process adaptability and
customer satisfactionbyrapid deliveryof working software product. - Agile Methods break the product into small incremental builds. These builds are provided in iterations.
- At the end of the iteration,
a working product is displayed to the customerand important stakeholders. - Flexible, Parallel, process divided into sprint
- Pros
* Frequently delivery
* Face-to-Face Communication with clients
* Anytime changes are acceptable
* It reduces total development time
Cons
* Less documentation
* Maintenance problem








